Understanding Deer Mice: The Adorable Yet Intriguing Creatures of Nature
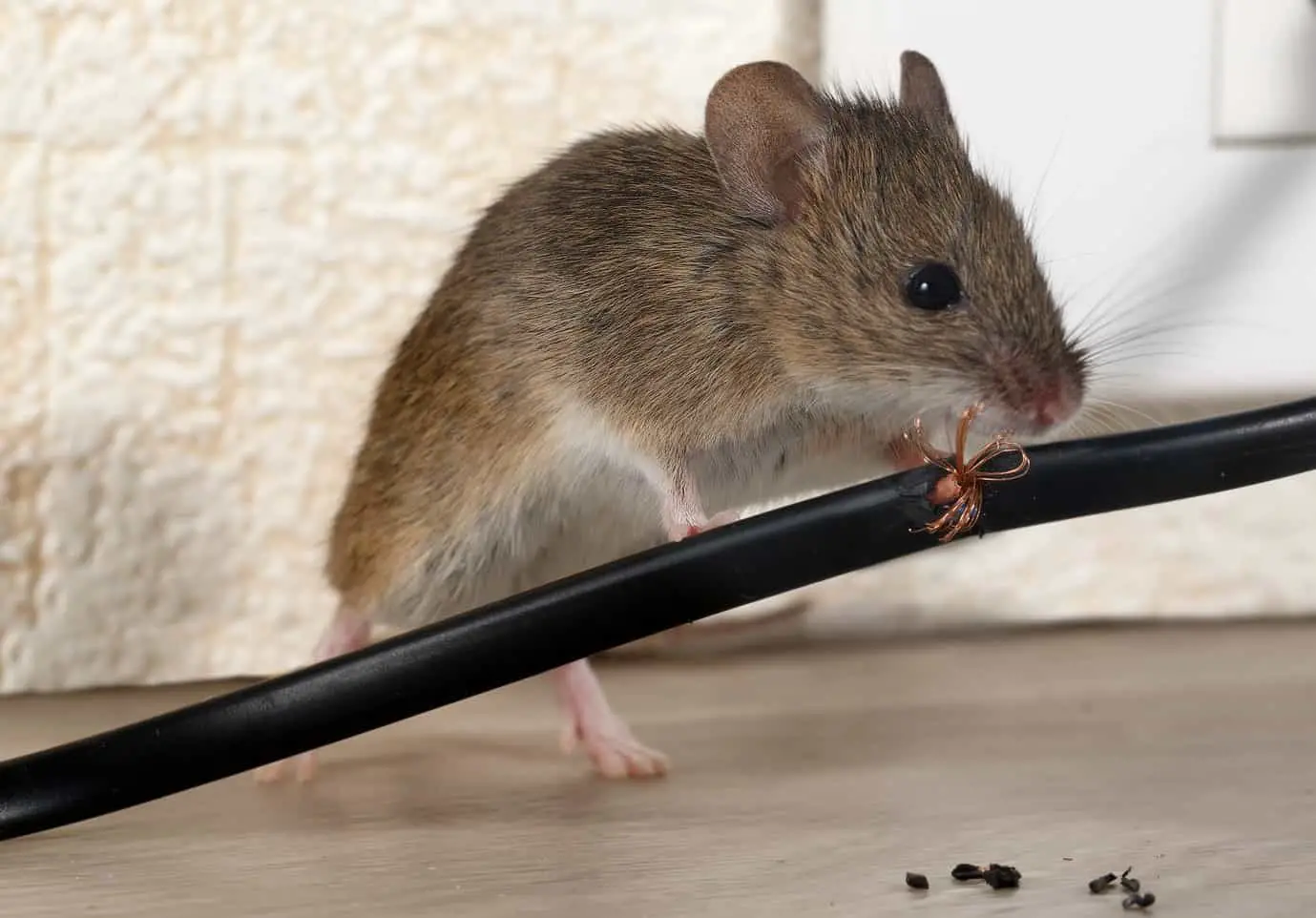

In the vast world of wildlife, one creature that often goes unnoticed but deserves our attention is the charming deer mouse (Peromyscus maniculatus). These small, agile rodents belong to the family Cricetidae and are native to North America. With their endearing appearance and fascinating behaviors, deer mice have managed to carve a special place in the ecosystem they inhabit. In this article, we will delve into the world of deer mice, exploring their characteristics, habitat, behavior, and ecological significance.
Appearance and Characteristics
Deer mice are distinguished by their enchanting features. Typically, they measure between 7 to 10 cm (2.7 to 3.9 inches) in length, with a tail spanning an additional 6 to 10 cm (2.3 to 3.9 inches). Their large, expressive eyes and large ears aid them in detecting predators and locating food. One of the most notable aspects of their appearance is their bi-colored tail, which showcases a striking contrast between the dark upper side and white underside.
These mice boast a wide range of colors, including shades of gray, brown, and reddish hues. Their fur often plays an essential role in camouflage, allowing them to blend seamlessly with their surroundings, making them less susceptible to predation.
Habitat and Range
Deer mice are incredibly adaptable rodents, found in diverse habitats across North America. From forests and grasslands to deserts and mountains, these little creatures have managed to thrive in various environments. Their distribution spans from Canada to Central America, displaying their ability to withstand different climates and conditions.
Behavior and Lifestyle
These nocturnal creatures are most active during the night, using their exceptional sense of smell and hearing to navigate their surroundings and locate food. Deer mice are omnivores, consuming seeds, fruits, insects, and even small vertebrates. Their diet’s versatility enables them to survive in regions where food availability fluctuates throughout the year.
During the day, deer mice retreat to their nests, which are usually constructed in burrows or hidden beneath logs, rocks, or vegetation. These nests provide them with a safe and secure environment, shielding them from potential predators.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Deer mice possess a rapid reproductive rate, with females often producing multiple litters during a single breeding season. The gestation period lasts around 23 days, after which a litter of typically 2 to 5 pups is born. These offspring mature quickly and are weaned within a few weeks. As a result of their reproductive efficiency, deer mice populations can increase rapidly under favorable conditions.
Ecological Significance
While deer mice may seem insignificant, they play a crucial role in their ecosystems. As seed and fruit eaters, they assist in seed dispersal, promoting plant growth and maintaining biodiversity. Moreover, they serve as prey for numerous predators, including birds of prey, snakes, and mammals like foxes and owls, helping to balance the predator-prey relationship.
Potential Threats and Conservation
Deer mice face various threats, primarily due to habitat destruction and fragmentation caused by human activities. Additionally, they may encounter challenges from introduced species that compete for resources. However, as of now, deer mice populations appear stable and are not considered endangered.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the unassuming deer mice, with their charming appearance and resilient nature, play an essential role in the intricate web of life in North America. Their ability to adapt, reproduce, and contribute to the ecosystem emphasizes their importance. By understanding and appreciating these small creatures, we can better protect and preserve the delicate balance of nature they are a part of. So, the next time you catch a glimpse of a deer mouse scurrying through the wilderness, take a moment to admire the beauty of this often overlooked but fascinating member of the animal kingdom.